

What is the purpose of a GeneMatch test?
All sperm donors used in fertility treatments are thoroughly screened for the most common, serious hereditary diseases to ensure they are healthy.
However, sperm banks cannot screen donors for all rare genetic mutations. Moreover, the donor only represents half of the equation – your own genes also play a significant role. A GeneMatch test examines whether your and the donor’s genes are a healthy match.

Gain peace of mind with a GeneMatch test
Humans have 2 copies of every gene – one from the biological mother and the other from the biological father.
We all carry an unknown number of genetic mutations without it leading to a genetic disease.
If both biological parents have mutations in the same gene, there is an increased risk of a recessive hereditary disease being passed on to the child.
Reduce the risk of
hereditary disease
To reduce this risk, we offer you the opportunity to take a GeneMatch test.
It is a comprehensive genetic test that analyses more than 400 recessive hereditary diseases in your genes and compares them with your potential donor’s genes.
Avoid mutations
in the same gene
The test can determine if both you and your donor have mutations in the same gene, thereby increasing the risk of your child inheriting one of these 400 genetic diseases.
With this answer in hand, you have a better opportunity to decide if the particular donor is the right match for you.
GeneMatch on Born sperm donors
For your treatment at Diers Klinik, you can select a GeneMatch for most of the available sperm donors from Born Donor Bank.
Currently, it is not possible to purchase a GeneMatch test for Livio’s donors through Diers Klinik.
If you want to order a gene compatibility test on one of the donors available with GeneMatch test, just click Buy GeneMatch and fill in the form.
What is the cost of checking compatibility with a sperm donor?
A GeneMatch test for one donor costs 1.125 €.
If there is not a good match with this donor, we offer you a new GeneMatch test with another donor for free, if you order the test within 1 week after receiving the results of the first GeneMatch test.
Expect to receive one of 3 specific results from the test
When you take a GeneMatch test with a potential donor, you will get one of the following 3 responses:

1. You and the donor are a good match:
This means you do not carry mutations in the same genes as your donor, and there is no risk of your child getting one of the more than 400 diseases screened for in the GeneMatch test.
Your report result will be: “No incompatibility is observed”.

2. You and the donor are not a good match:
Both you and the potential donor carry mutations in the same gene. This means you risk transmitting a hereditary disease to the future child if you choose this donor.
Your report result will be: “Incompatibility is observed”. In this case, we recommend that you choose a different donor and take a new GeneMatch test.

3. You have an X-linked disease:
One of your X chromosomes has a disease causing mutation in a gene. This may lead to a hereditary disease in your child if it’s a boy.
You will be informed in the test response about which gene it is. Your choice of donor has no influence on this.
You should seek genetic counselling for your further fertility journey, as there is a high risk of passing on the affected X chromosome. Diers Clinic cannot offer this counselling.
How do I get a GeneMatch test?
To get a GeneMatch test, just click Buy GeneMatch and fill in the form.
We will then send you a test kit for you to provide a saliva sample, which the testing laboratory will use to analyse your genes. The test is conducted by Bioarray, a Spanish testing laboratory.
Taking the test is simple:
- Collect a saliva sample following the instructions in the test kit.
- Sign the included consent form.
- Place the saliva sample, consent form, and the provided requisition form into the included return envelope.
- Arrange for the return envelope to be collected by courier as directed in the test kit.
- The courier will deliver the envelope to the testing laboratory.
It takes up to 6 weeks to receive a response from the test laboratory, and we will email the result to you as soon as we receive it.
Secure your favourite donor before GeneMatch test results
To prevent your preferred donor’s sperm units from selling out while you await the test results, we recommend purchasing sperm units from your preferred donor and having them stored with us in a donor sperm storage.
We suggest buying 1-3 donor units for storage. Once you have the genetic match test results, you may add more units to your storage if desired.
If the genetic match test indicates that you are not compatible with the selected donor, we offer a free exchange (up to 3 donor units) for a similar donor within the same category who has units available for exchange. This offer for a free exchange is valid for 3 months from the date of the sperm purchase.
GeneMatch – Step by step
Here is the procedure for the GeneMatch test:

Check if your donor offers GeneMatch testing on our our donor list. Purchase a test by clicking here.

We will send an invoice, and once payment is received, we’ll ship the test kit.

Take a saliva sample according to the instructions in the test kit and sign the enclosed consent form.

Send the response envelope with the saliva sample, the consent form and the requisition form to the test laboratory by courier as instructed in the test kit.

The laboratory analyses the samples, and the test result is ready within 6 weeks.

You will receive a reply from us by e-mail.
Explanation of Genetic Diseases
Learn more about the heritability of genetic diseases and why we test for compatibility.
Humans have 46 chromosomes, which come in pairs. There are two sex chromosomes (X and Y) and the rest are called autosomes. Egg and sperm cells contain 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome each. Genes are distributed across these chromosomes and are referred to as either sex-linked genes or autosomal genes.
Humans have about 30,000 active genes, and we inherit two copies of each gene – one from our biological mother and one from our biological father.
We can have mutations in one gene without symptoms, which means we carry a recessive genetic disease. If both the gene from the biological mother and the gene from the biological father are mutated, a recessive disease can develop. Here, a GeneMatch test is useful.
Genetic diseases are divided into autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, X-linked, or Y-linked diseases. Below, we will explain these categories and which diseases the GeneMatch test checks for.

Autosomal Recessive Genetic Diseases
An autosomal recessive disease occurs only if both copies of a gene are mutated. This means that both biological parents must carry the mutation for the disease to be transmitted. Therefore, it is important that both you and your donor get tested.
If both parents have the same mutation, there is a 50% chance that a child will be a carrier of the mutation (a healthy copy from the biological mother and a mutated copy from the biological father or vice versa), a 25% chance that they will not inherit it (a healthy copy from both parents), and a 25% chance that they inherit both mutated genes and develop the disease (a mutated copy from each parent).
If the GeneMatch test shows incompatibility with the donor, there is a 25% chance that your child will inherit an autosomal recessive disease with that donor.

Autosomal Dominant Genetic Diseases
An autosomal dominant disease occurs if one copy of a gene is mutated. This means that one of the biological parents must carry the mutated gene, and as a result, the individual will also be affected by the disease. Other family members will often have the same disease.
Sperm banks thoroughly screen all donors for autosomal dominant diseases during the approval process, which is why no further testing is conducted for this type of genetic disorders.
X- and Y-Linked Genetic Diseases
X- and Y-linked diseases affect the genes on the X and Y sex chromosomes, respectively. Women and men have different sets of sex chromosomes – XX and XY. Women inherit an X chromosome from each parent, while men inherit an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the father.
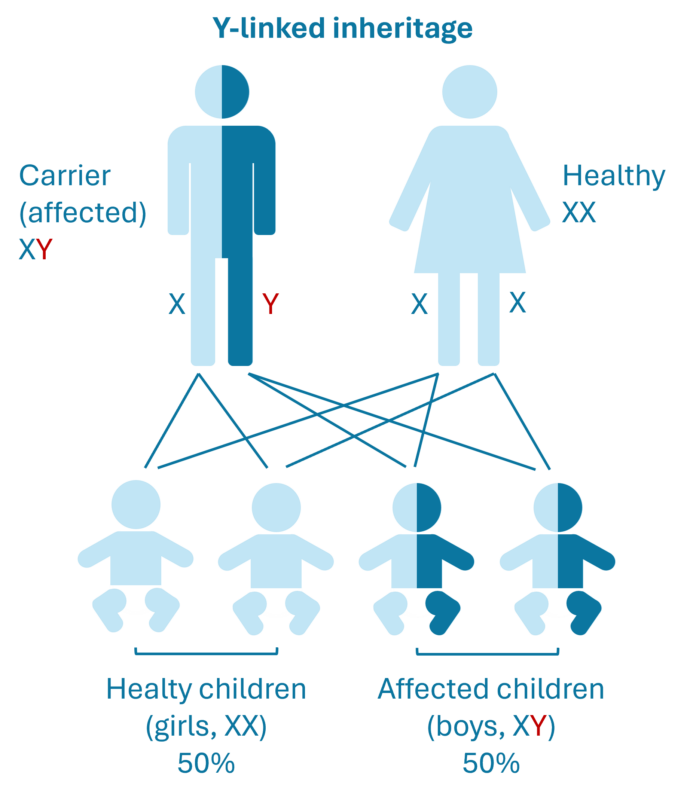
Y-linked diseases: Occur only in male children. The Y chromosome is passed from the biological father. The donor is screened for hereditary diseases, so further investigation for Y-linked diseases is not conducted.
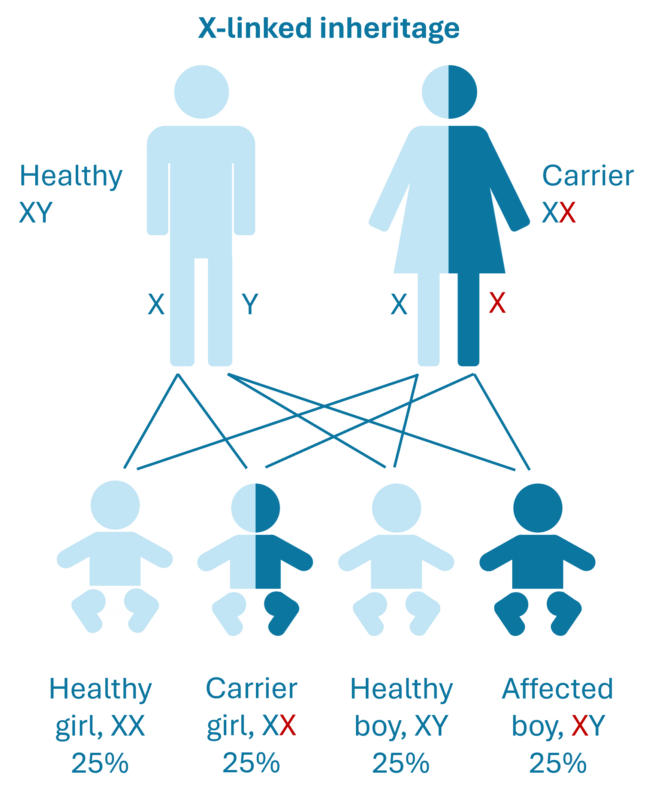
X-linked diseases: These are rare in women, as they require the same mutated gene from both parents. Men have only one X chromosome, inherited from the mother, and can develop X-linked diseases if they inherit a mutated gene from the mother. There is a 50% risk of passing the disease gene to the child. A GeneMatch test therefore warns of certain X-linked mutations you as a mother might have.
FAQ
The fact is that we all carry an unknown number of recessive gene variants (mutations) that can be passed on to our children. Most of us are unaware of what we carry and never experience any symptoms.
If both biological parents carry a variation in the same gene, there is an increased risk that the child will develop a disease. The risk is the same for all children, whether conceived with donor sperm or not.
Even though sperm donors are thoroughly screened, there is still a small risk that the child will inherit a disease, and the risk is greater if both the sperm donor and the biological mother carry a variation in the same gene.
If you want to be on the safe side and significantly reduce this risk before getting pregnant, GeneMatch is the right choice for you. With this test, we match your genes against the donor’s to see if you are genetically compatible.
Generally, the chance of biological parents transmitting a recessive disease to their child is about 1 out of 100, or 1%. For women, the risk of being a carrier of an X-linked disease is up to 1 out of 200, corresponding to 0.5%.
No. Although we match you and your chosen donor and check for a very large number of recessive diseases, we cannot 100% guarantee that your child will not have a genetic disease. There will always be a small remaining risk because we do not test all genes and because newly arisen or unknown mutations cannot always be detected by matching.
The price for a GeneMatch test with a single donor is 1125 Euro. If there is not a good match, you get the next GeneMatch test for free, if you order the test within 1 week after receiving the results of the first test.
Yes, if you follow the instructions in the kit and fill the collection container to the “fill line”, there will be enough material for a genetic test. In some cases, a new sample may be required if the material is not of adequate quality.
No, you will not receive a genetic profile or other detailed review of your full genetic profile. You will only receive an answer on whether your and the donor’s genes are a healthy match, i.e., there is no risk of passing on one of the over 400 recessive hereditary diseases screened for with the GeneMatch test.
You have a mutation in the same gene as the donor, but neither of you is sick. You should choose a different donor, as there is a 25% risk of having a sick child. It is not uncommon to have mutations in one or more genes. Diers Klinik is not informed which gene the mutation is found in and therefore cannot provide further information about the specific mutation.
No, the test laboratory does not need a new saliva sample. The laboratory can reuse the genetic material from the previous saliva sample if you order within 1 week after receiving the results of the first test. You can expect to receive the result of the second test already within 48 hours.
You will be informed in the test result which X-linked disease it concerns. You should seek genetic counselling before proceeding with fertility treatment, as there is a high risk of passing the diseased X chromosome to your future child.
Yes, but the blood sample must be collected at our clinic. Please contact the clinic if you wish to have a blood sample taken for the GeneMatch test instead of submitting a saliva sample yourself.